
RTM Locker is the current enterprise-targeting ransomware operation discovered to be releasing a Linux encryptor that targets virtual makers on VMware ESXi servers.
The RTM (Check Out The Manual) cybercrime gang has actually been active in monetary scams because a minimum of 2015, understood for dispersing a custom-made banking trojan utilized to take cash from victims.
This month, cybersecurity company Trellix reported that RTM Locker had actually released a brand-new Ransomware-as-a-Service (Raas) operation and had actually started to hire affiliates, consisting of those from the previous Conti cybercrime distribute
” The ‘Check out The Handbook’ Locker gang utilizes affiliates to ransom victims, all of whom are required to follow the gang’s rigorous guidelines,” discusses Trellix
” The business-like establish of the group, where affiliates are needed to stay active or inform the gang of their leave, reveals the organizational maturity of the group, as has actually likewise been observed in other groups, such as Conti.”

Security scientist MalwareHunterTeam likewise shared a sample of RTM Locker with BleepingComputer in December 2022, suggesting this RaaS has actually been active for a minimum of 5 months.
At the time, Trellix and MalwareHunterTeam had actually just seen a Windows ransomware encryptor, however as Uptycs reported the other day, RTM has actually broadened its targeting to Linux and VMware ESXi servers.
Targeting VMware ESXi
Over the previous years, the business has actually relocated to virtual makers (VMs) as they provide enhanced gadget management and a lot more effective resource handling. Due to this, a company’s servers are typically topped a mix of devoted gadgets and VMware ESXi servers running several virtual servers.
Ransomware operations have actually followed this pattern and developed Linux encryptors committed to targeting ESXi servers to secure all information utilized by the business correctly.
BleepingComputer has actually seen this with nearly all enterprise-targeting ransomware operations, consisting of Royal, Black Basta, LockBit, BlackMatter, AvosLocker, REvil, HelloKitty, RansomEXX, Hive, and now, RTM Locker.
In a brand-new report by Uptycs, scientists evaluated a Linux version of the RTM Locker that is based upon the dripped source code of the now-defunct Babuk ransomware.
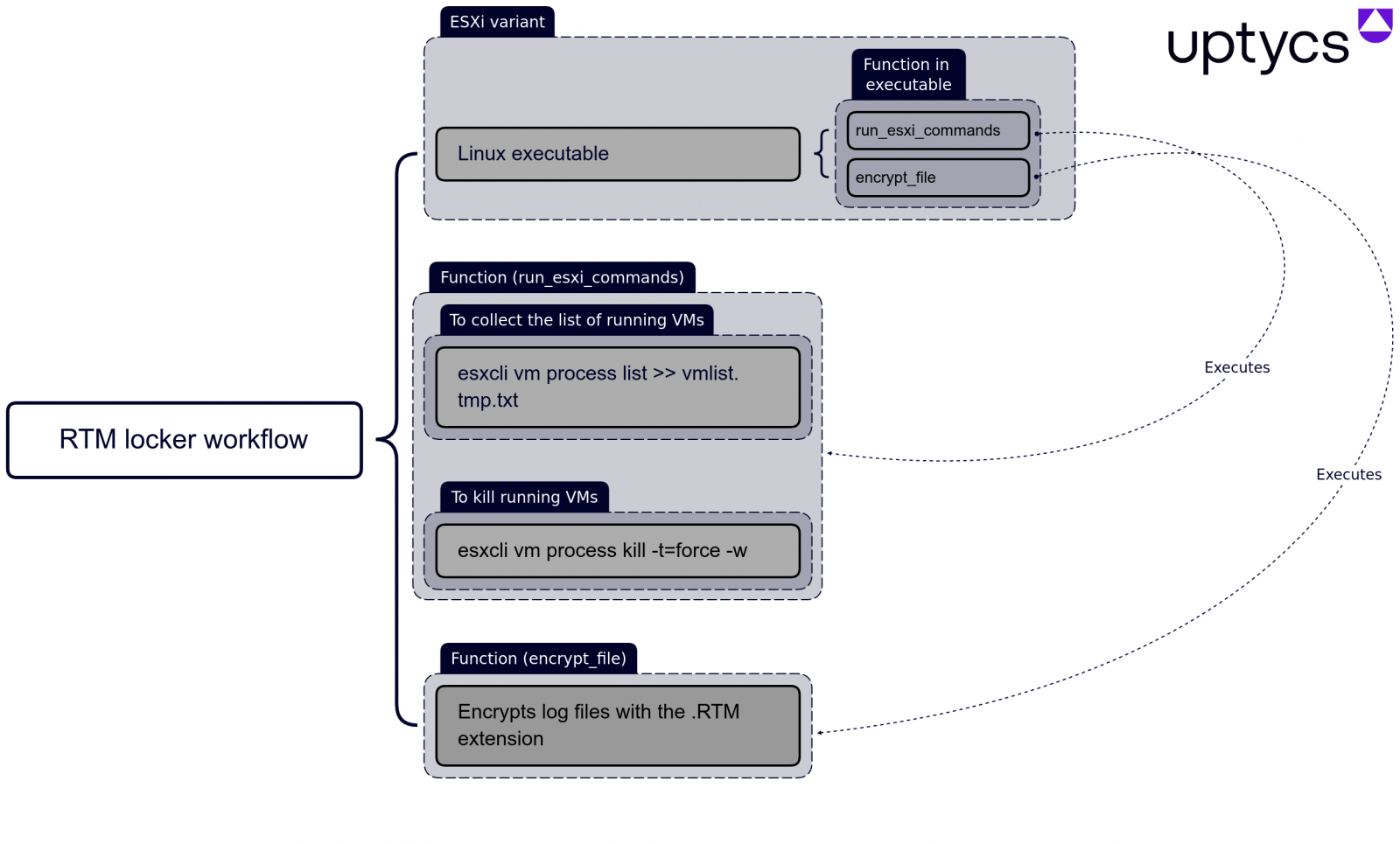
The RTM Locker Linux encryptor seems developed clearly for assaulting VMware ESXi systems, as it includes many referrals to commands utilized to handle virtual makers.
When released, the encryptor will initially try to secure all VMware ESXi virtual makers by very first collecting a list of running VMs utilizing the following esxcli command:
esxcli vm procedure list >> > > vmlist.tmp.txt
.(* )The encryptor then ends all running virtual makers utilizing the following command: esxcli vm procedure kill -t= force -w
After all the VMs are ended, the encryptor starts to secure files that have the following file extensions -. log (log files),. vmdk (virtual disks),. vmem (virtual maker memory),. vswp (swap files), and.vmsn (VM photos).All of these files are connected with virtual makers working on VMware ESXi.
RTM’s attack workflow
The outcome is safe and secure and hasn’t been broken yet, so there are no readily available totally free decryptors for RTM Locker at this time.
Uptycs likewise comments that the cryptographic algorithms are “statically carried out” into the binary’s code, making the file encryption procedure more trusted.
When securing files, the encryptor adds the
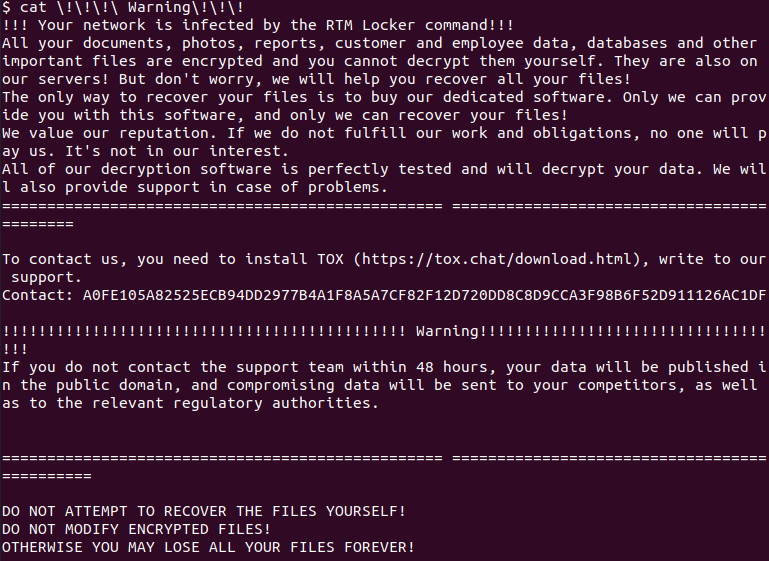
RTM file extension to encrypted file’s names, and after it’s done, develops ransom notes called !!! Caution!!! on the contaminated system. The notes threaten to call RTM’s “assistance” within two days through Tox to work out a ransom payment, or the victim’s taken information will be released.
RTM ransom note sample
nvfutdbq3ubteaxj4m2jyihov5aa4akfudsj5h7vhyrvfarfra26ksyd.onion
.
3wugtklp46ufx7dnr6j5cd6ate7wnvnivsyvwuni7hqcqt7hm5r72nid. onion
The presence of an ESXi-targeting variation suffices to classify RTM Locker as a considerable risk to the business.Nevertheless, fortunately is that BleepingComputer’s research study has actually revealed that the group is not especially active, though that might alter in the future.